Checking the logs and downloading CSV/TSV "snapshots"
- Getting Started
- General Guides
- Quick Start (GUI)
- Setup a Standard Job (GUI)
- Setup a Standard Job (Headlessly)
- Setup a Port Job (GUI)
- Setup a Port Job (Headlessly)
- Setup a GIS Job (GUI)
- Setup a GIS Job (Headlessly)
- Additional Resources
- Control File Config
- Preferences Config
- Scheduling a Job
- Checking Logs
- FAQ / Common Problems
- Network Considerations
- Data Conditions & Restrictions
- Using the Map Fields Dialog
- Developer Guides
- DataSync Library/SDK (Java)
- Compiling on Windows (with Eclipse)
- Compiling with Maven
Contents
- Via the Platform UI
- [navigating to
/admin/jobs](#navigating-to-the-logs) - debuging the actual logs
- [navigating to
- Via FTP
- Via HTTP
Customers who are using DataSync via FTP or HTTP can get detailed debugging information by retrieving the logs for each job. Details of how to access those logs can be found below.
Checking /admin/jobs
Customers can use the UI to get to a jobs status page that will tell them the status of the 250 most current jobs and get detailed information on their success or failure. They get there by navigating to it from the admin panel on thier open data portal instance.
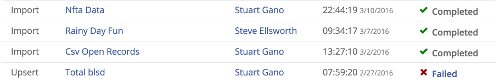
The feilds that are exposed through this are: success/failure, publish method, dataset owner, and a timestamp.
When a job fails you can click on it to get more details and see some error messaging on what may have been wrong on upload. The below is a sample error message for a job that had a record that could not be identified as a date type in one of the columns.
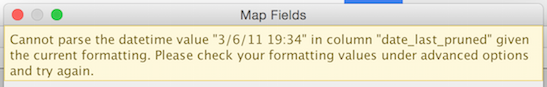
Connecting to the logs via FTP
Connecting to the FTP server
You can use Filezilla or any other FTP client that supports FTPS to connect to the FTP server.
In Filezilla go to File -> Site Manager.
Set up a new connection with the following details:
- Host: production.ftp.socrata.net
- Port: 22222
- Protocol: FTP
- Encryption: Require explicitly FTP over TLS
- User:
<Your Socrata username> - Password:
<Your Socrata password>
Ensure the transfer mode is ‘Passive’ by going to:
Transfer Settings -> Transfer mode : Passive.
Save the connection and press “Connect”.
If you only have permission to one domain, you will be dropped into the directory for that domain. You should see the directories named with the dataset ID (e.g. b2fd-cjk2) of any dataset you have updated using DataSync replace via FTP. If you have permission to multiple domains, you will see them as subdirectories.
Checking the logs and downloading CSV “snapshots” when using FTP
Inside each dataset identifier directory there should be the following files/directories:
- active-control.json
- log.txt
- status.txt
- completed
You can download log.txt to see the logging information for the given dataset. Within the ‘completed’ directory you can find CSVs/TSVs and control.json files archived by date (there are nested folders for year, month, and day). After each successful update operation using DataSync replace via FTP, the CSV/TSV and control.json files that were used to perform the update are archived. Archived files will are stored for 30 days. Contact Socrata support if you would like additonal information about archiving.
Connecting to the logs via HTTP
Checking the logs
You must be signed in with an account with publisher rights before you can view the logs. Logs are offered in a plain text form or in a json format by using either the first or second url in each pair below respectively.
Logs for all DataSync over HTTP jobs run on your domain by visiting:
https://<Your domain>/datasync/log
https://<Your domain>/datasync/log/index.json
DataSync logs for a specific dataset can be found by visiting:
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/log/
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/log/index.json
The status of an in-progress job on a specific dataset can be found by visiting:
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/status/
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/status/index.json
DataSync logs for a specific job can be found by visiting
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/log/<Your job ID>
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your dataset ID>/log/<Your job ID>.json
Where
<Your domain> is your domain, <Your dataset ID> is the identifier of the dataset and <Your job ID> is the identifier of the job. The job identifier is a 32-length character string and is included in all of the logs listed above.
Downloading CSV “snapshots” when using HTTP
Each CSV uploaded through DataSync over HTTP is available for at least 30 days after upload. The CSV can be found by generating a URL with the following pattern
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your Dataset ID>/completed/yyyy/mm/dd/hh:mm:ss.xxx-<Your file name>.csv
Where <Your domain> is your domain, <Your dataset ID> is the identifier of the dataset and <Your file name> is the name of the CSV you uploaded.
The date information within the path can be found by navigating the /completed/ directory. For example, to see which months still contain snapshots, you can use:
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your Dataset ID>/completed/yyyy/
And to determine the complete file name, including the hour, minute, seconds and milliseconds, you can use
https://<Your domain>/datasync/id/<Your Dataset ID>/completed/yyyy/mm/dd/
noting that the resulting file will be url-encoded.